When it comes to graphene, netizens will surely think of the Nikkei posts in the computer and battery industries. But a research team at Rice University found another application for it - converting carbon dioxide to liquid fuel. The core part of this technology is "N-doped graphene quantum dots" (NGQDs), which can be used as "electrochemical reaction catalysts" in the production of ethylene and ethanol, with stability and efficiency close to the most common copper, etc. material.

Rice University researchers have used "N-doped graphene quantum dots" to convert carbon dioxide to liquid hydrocarbons (such as ethylene and ethanol that can be used as fuel).
To mitigate the impact of climate change, reducing carbon dioxide emissions into the atmosphere is a very important approach.
Many studies are looking for ways to capture carbon sources and use clays, engineered bacteria, metal-organic frameworks, or Memzyme bubble materials, which are then sealed into rock or concrete.
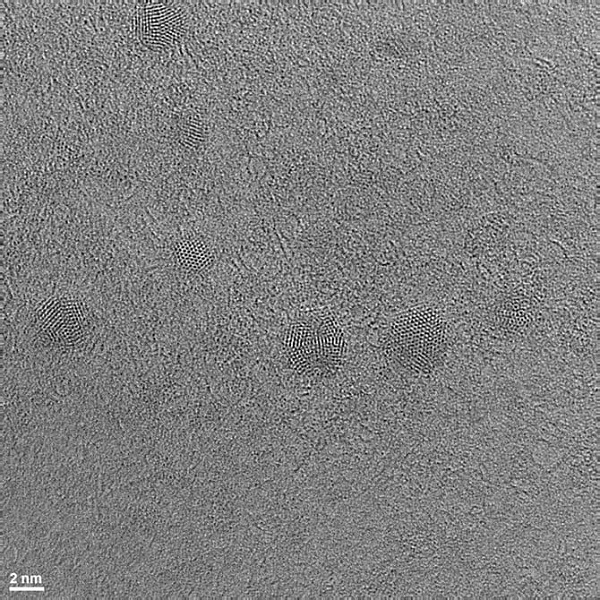

At this scale, the "N-doped graphene quantum dots" on the substrate look like a circular patch pattern.
There is also research focused on how to capture carbon sources and convert them into liquid hydrocarbons (and then as fuel), and researchers at Rice University found that NGQDs are a highly efficient electronic catalyst material.
The material is a single-layer atomic-thick graphene sheet, and the dots above are only a few nanometers wide. Because it is itself an all-carbon material, it cannot convert carbon dioxide on its own, so the researchers doped it with nitrogen atoms to stimulate the electrochemical reaction of carbon dioxide.
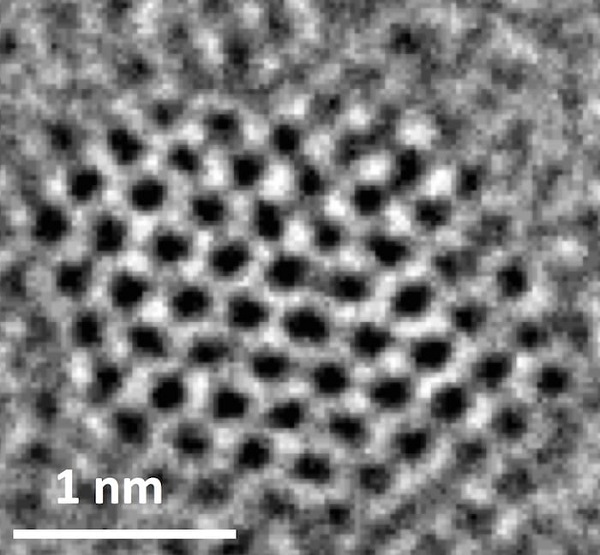
The figure above shows the appearance of a single "N-doped graphene quantum dot."
Research chief Pulickel Ajayan said: "Carbon is not usually a catalyst. We are shocked by how effective it is. When it is doped into a hexagonal graphite lattice, there are many nitrogen atoms that can occupy it."
"According to the location of nitrogen, its catalytic activity is not the same, which is a mystery to us. Even if people wrote numerous papers in the past 5-10 years, this problem has not been truly solved."

The "N-doped graphene quantum dots" under transmission electron microscope images are also used in the process of converting carbon dioxide into fuel.
Although the mystery has not yet been revealed, we still tested a variety of electronic catalyst materials. Under the background of rising copper prices, they are expected to become major competitors, but efficiency is still the most valued.
NQGDs have been found to have about the same efficiency as copper (a 90% reduction in carbon emissions), capable of converting the 45% of the carbon they capture into ethylene and ethanol fuels, and have a longer lifespan.
Details of this study have been published in the recently published Nature Communications journal.
Diamond Wire For Magnetic Material Cutting
When the electroplated Diamond Wire is cut, the workpiece is scratched by the diamond abrasive particles on the circumferential surface. Electroplated diamond wire cutting is widely used in the field of hard and brittle material processing due to its high cutting efficiency and little damage to raw materials. Compared with other hard and brittle materials, magnetic materials such as neodymium, iron and boron have similarities and differences. Magnetic materials such as neodymium, iron and boron are mostly made by powder metallurgy process, and there are large lattices and voids inside the materials. It has a certain influence on the electroplated diamond cutting wire.
Diamond Wire for Magnetic Material,Diamond Wire Magnetic Material Cutting,Diamond Wire Cutting Magnetic Material
Jiangyin Baoneng Precision New Material Co.,LTD , https://www.baonengwire.com