Abstract: Introduction CNC machine tools are being widely used in various fields of manufacturing. Software plays an important role in CNC machine tools, and its user interface directly affects the efficiency and effectiveness of CNC machine tools. Therefore, designing the software user interface of CNC machine tools becomes more and more important under the consideration of human factors.
Introduction CNC machine tools are being widely used in various fields of manufacturing. Software plays an important role in CNC machine tools, and its user interface directly affects the efficiency and effectiveness of CNC machine tools. Therefore, designing the software user interface of CNC machine tools becomes more and more important under the consideration of human factors.
This paper analyzes the software user interface of CNC machine tools (using CNC5000V200Milling) from the perspective of human cognition psychology, user usage and menu semantic structure system, points out the existing problems, and proposes a solution to the problem.
Software user interface of CNC drilling machine CNC5000V200
Figure 1 Software user interface of CNC drilling machine CNC5000V200
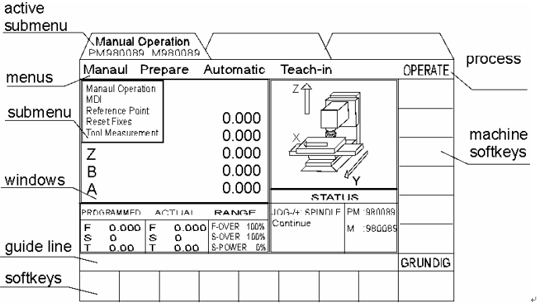
The control system software of CNC drilling machine CNC5000V200 has a graphical interface, as shown in Figure 1. The interface has three function-independent processes (PROCESS): OPEARTE, PROGRAM, CONTROL. Each process serves the system's operators, programmers, and system monitors (SUPERVISOR).
Highlights indicate the processes and modes that are activated. The activated process has its own color and is displayed as the foreground of the screen. For example, OPERATE corresponds to green, PROGRAM corresponds to dark blue, and CONTROL corresponds to light blue.
Each process has its own menu line, and the menu on the menu line is a drop-down menu with its own submenu. The submenu can be selected for the next step.
The individual softkey functions displayed in the soft keypad depend on the activated process and menu mode. The boot line shows information about how the user is going to do the next step. By pressing the HELP key, a brief explanation of the user's operation error can be displayed.
The CNC softkey area shows the special machine functions developed by the machine tool builder. They can be activated via soft keys. A sketch of a CNC machine shows the direction of each axis.
The windows can be opened at a fixed position on the screen, and they display different information such as menus, text, programs, tables, and graphics. Their size and form depend on the process, menu and submenu being activated.
Analysis of CNC5000V200 software interface of CNC drilling machine The basic problems of software user interface design are:
Determine the content of information that is communicated between the person and the computer that should be displayed on the screen in order to complete the tasks of the software system.
Determine the display form of the above information.
In this article, we will analyze and evaluate the solution effect of CNC drilling machine CNC5000V200 software interface on the above problems from the perspective of human cognition psychology, user usage and menu semantic structure system, and point out the problems and solutions of the software interface. The method of the problem.

In terms of human information processing, Rasmussen proposed a multi-level cognitive control model in 1983: SRK theory. SRK believes that:
1) People use three levels of cognitive control to process information, namely: Skill-Based Behaviour (SBB), Rule-Based Behaviour (RBB), knowledge-based The Behavior-Based Behaviour (KBB) is shown in Figure 2.
2) These three levels can be divided into two categories: SBB and RBB handle feelings and actions, while KBB processes solve problems based on symbolic representation. In general, lower-level behaviors of cognitive control can be accomplished more efficiently and with less effort than higher-level behaviors. Therefore, people prefer to use lower levels of cognitive control behavior.
3) The requirements of the task, the experience of the user, and the way in which the information is displayed collectively determine which cognitive control level behavior is activated.
4) The goal of interface design is that the designed interface should not be forced to activate higher levels of cognitive control than required by the task, and should also provide information support for all three cognitive control level behaviors.
1.2 CNC Drilling Machine CNC2000V200 Software User Interface Human Cognitive Psychology Analysis 1) Analysis from KBB Problem There is no information indicating the interface structure from the overall perspective on the software interface. For example, there is no indication of the relationship between the three processes of OPERATE, PROGRAM and CONTROL, and the relationship between the various menus and the submenus. This makes it difficult for the user to grasp the structure of the interface from a holistic perspective and solve the problems encountered in learning and use.
Analysis Users can be divided into primary users, intermediate users and advanced users. For beginners, most of the interface is new, they must learn and master it through KBB, but there is no information on the interface to support KBB, so it is difficult for the primary user to establish the basic structure of the interface from a holistic perspective.
For mid-level users, even advanced users will encounter new problems when using the interface. In order to solve these new problems, they must activate KBB. In this way, they have to work hard to imagine the structure of the interface in their minds to support KBB, because there is no such information on the interface. Therefore, it will increase the user's memory burden and the difficulty of solving the problem.
2) Analysis from the perspective of RBB On the interface, there is no operation sequence information for common tasks, which makes the primary and intermediate users feel difficult to complete common tasks.
Analysis The function of RBB is to organize a sequence of operations when a user faces a task. This sequence of operations is either from previous experience or learned from others or via KBB. RBB needs a support for information on the sequence of operations for common tasks when doing this. There is no such information on this interface. For example, there is no information showing how the user completes the sequence of operations for programming the part program, ie:
Program the part program = OERATE-Reference Point-Program-Part program-Operate-Automatic (Dry-Run, or Wire Plot Graphic or Program Check).
The information of the interface boot line only shows the operations that the user can choose next. For example, in the PROGRAM-Part Program-Main Program mode, the boot line is displayed as:
Give program number
Such information is of little help to junior and intermediate users because they do not yet know the main sequence of operations to accomplish this task.
3) Analysis from the perspective of SBB Problem This interface does not provide users with operable continuous spatiotemporal signals, which makes it difficult for users to rely on SBB as much as possible, especially for beginners. This greatly reduces the efficiency and comfort of the operation.
4) Summary From the perspective of SBK theory, this interface has the following problems:
It is difficult for users to grasp the structure of the interface from a holistic perspective and solve the problems encountered in learning and use.
Beginner and intermediate users find it difficult to complete common tasks.
It is difficult for beginners to rely on SBB, which greatly reduces the efficiency and comfort of the operation.
5) Solution For the above problems, the software interface should provide users with:
The software system structure is displayed in an organized network diagram to support the user's KBB.
Display a sequence of function-oriented operations in a sequence diagram. To support the user's RBB
On the hardware interface, the user is provided with an input device capable of generating a continuous spatiotemporal signal, such as a mouse, to activate the human SBB as much as possible.
2. Analysis from the user's point of view 2.1 User classification According to the user's background knowledge in the task field (CNC machining field) and computer field, users can be divided into primary users, intermediate users and advanced users.
Primary users This group has less knowledge of the computer field. They have a fear of learning and using computers, can't grasp the overall structure of the interface system, and can complete simple tasks with the help of others.
The intermediate user group has certain background knowledge in the task field (the field of numerical control processing) and the computer field. They have an understanding of the interface within a certain range, can complete the basic tasks, and can complete more complicated tasks with the help of HELP. .
Advanced users These users have a very rich background in the field of tasks (CNC machining) and computers, and they are eager to improve the efficiency of using software.
2.2 Analysis The interface should be suitable for these three types of users, and support the transition from primary users to intermediate users, and the transition from intermediate users to advanced users.
1) Analysis from the perspective of the junior and intermediate users From the perspective of the junior and intermediate users, the interface of the CNC machine software has both shortcomings and advantages.
The advantage is that this interface provides ASSISTED ENTRY MODE and DIALOG ENTRY MODE for the initial and intermediate users under the process PROGRAM, which makes user programming very easy and convenient, and ASSISTED ENTRY MODE can also promote intermediate users to advanced users.
The disadvantage is that there are many terms and icons on the interface that are not explained, which makes it difficult for users, especially the novice users, to understand its exact meaning, such as "ACTIVE FUNCTION".
2) Analysis from the perspective of advanced users This interface provides advanced users with FREE ENTRY MODE to meet their desire to improve their work efficiency.
However, there are still some problems here. For example, under FREE ENTRY MODE, the user must press the ENTER key for each data input, which brings a lot of trouble to the user.
3) Summary From the user's point of view, this interface has the following problems:
Due to the lack of information on the interface, users, especially primary users, have difficulty understanding the meaning of terms and icons on the interface.
For advanced users, there are some lengthy operations on this interface.
4) Solution On the interface, add the necessary explanations for terms and icons.
Provides more streamlined operations for advanced users.
3 From the perspective of menu semantic structure The CNC drilling machine CNC5000V200 software user interface consists of menus, windows, soft keys, guide lines and online help. Here, only the menu semantic structure is analyzed.
3.1 About the menu system The main goal of the menu system design is to create a menu system that is visible, easy to understand and memorable, and easy to operate. At the same time, the menu system should also support the user's task of thinking about his door and enable them to easily organize task-oriented sequences of operations.
The key to menu design is to organize the semantic structure of the menu from the user's perspective as much as possible.
3.2 Menu Semantic Structure Analysis In order to analyze and evaluate the menu semantic structure system of the interface, the difference between the CNC drilling machine CNC5000V200 software user interface menu semantic structure system and the CNC drilling machine CNC5000V200 software user interface menu structure system organized from the user's point of view was found. We designed the following experiment.
In this experiment, all menu terms and their explanations on the CNC5000V200 software user interface of the CNC drilling machine are randomly listed in sequence, such as:
Reference Point: The position of the machine spindle is measured relative to this point.
Table: Tool position definition number type Graphic compensation size Status tolerance data is stored here.
··· ···
Then, 20 teachers from the NC machining teaching and research section and senior students who have studied the CNC machining course were invited to participate in the test (these subjects had extensive knowledge in the field of CNC machining, but did not touch the CNC drilling machine CNC5000V200 software user interface), and required the participants. Carefully read all the menu terms and explanations of the CNC drilling machine CNC5000V200 software user interface, and then ask them to re-establish the menu semantic structure system of the CNC drilling machine software user interface from their own perspective.
Figure 3 menu semantic structure system consistency comparison statistics table

1) Experimental results By comparing the CNC drilling machine CNC5000V200 software user interface menu semantic structure system and the menu semantic structure system of the CNC drilling machine software user interface re-established by the testee, we obtained the statistical results of the consistency between the two menu systems, such as Figure 3.
2) Analysis of experimental results Generally speaking, if there is a clear logical relationship or the same vocabulary between menus and submenus, the consistency of such menu semantic structure is high, such as: Manual Manual Operation Program Main Program Macro Program
Conversely, the consistency of the menu semantic structure system is low. For example, the consistency of the Automation group is only 1%. In the CNC drilling machine CNC2000V200 software user interface menu semantic system, Automation includes the following submenus: Machining, Dry Run, Wire Plot Graphics, Program Check, Erase Graphics.
3) Conclusion It is very difficult to design a menu semantic structure system that is completely consistent with the user's psychology from a logical point of view.
The naming of submenus directly affects consistency. The submenu naming is especially important when a submenu can logically belong to several main menus at the same time. If the submenu has the same vocabulary as the main menu to which it belongs, the affiliation of the submenu can be made affirmative, otherwise it will lead to confusion.
The appearance of the same or similar vocabulary in a unified level menu can make the user feel the menu system is confusing.
4) Solution Design the semantic system of the menu from the user's perspective as much as possible.
Do not apply the same or similar vocabulary at the same menu level.
Apply the same or similar vocabulary to the Ownership menu and submenu.
Based on the above analysis, we believe that the human factor in the CNC2000V200 software user interface of CNC drilling machine is rarely considered, which seriously affects the user's learning and use of the software.
LED Solar Light,High Quality LED Solar Light,LED Solar Light Details, CN
SHENGYA LIGHTING TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD. , https://www.syalighting.com