Today's introduction is mainly divided into three aspects. Firstly, the mechanical model and force relationship of the fasteners will be introduced. Then, how to measure the friction coefficient of the fasteners and the current standards will be introduced. The third part will introduce the current tightening and friction. The relationship of the coefficients, how the coefficient of friction affects the effect of the assembly.
The picture below shows the basic working principle of the fastener. The principle of the fastener is that through two or more parts, the bolts are used to link them together without relative sliding. This is the fastening. The most important function of the piece; in terms of use, the clamping force of the fastener or the axial force is the most important factor in the use of the fastener.
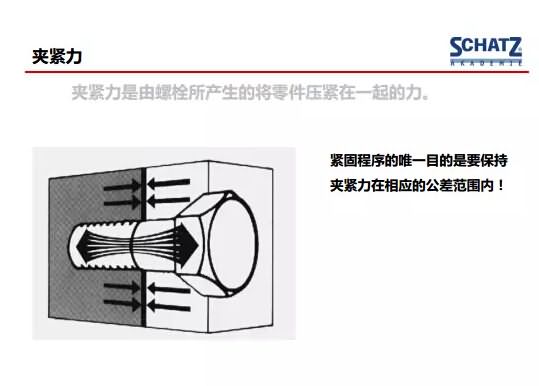
The clamping force generated by the fastener must be within a reasonable and safe tolerance range for the fastener to work properly. If the clamping force is too large, the bolt may stretch too long, so that fatigue fracture occurs in advance; if the bolt clamping force is too small, it is not enough to press the parts together, looseness may occur, and the bolt may be broken. Therefore, the most challenging part of the tightening and tightening design is how to control the clamping force of the bolt fastener.
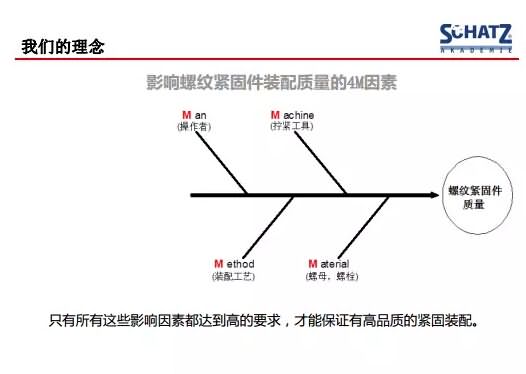
The following picture is the German Schatz company's understanding of the bolt tightening method, referred to as four M, only the four M control, in order to have a perfect assembly of the product, these four M represent:
The first Ma, the operator, we tighten the field, or the bolt designer needs to have a good fastener base and receive the correct training;
The second M, Material, whether it is a connector bolt, nut or connected piece, the grade and choice of material should be in line with the best design;
The third M, Method, tightening or tightening strategy, each fastener must be selected to match their tightening strategy or process;
The fourth M, Machine, tightens the tool, which is often overlooked. We focus on fasteners that tend to focus on materials and tightening tools. Sometimes the effectiveness of the site is often due to the wrong tightening tool we chose, or we tighten The tool did not choose to be caused by the timely target.
The next picture is the model of the force analysis. In the stress analysis of the whole fastener, the force of the bolt is not uniform, but there are different places where the hard force is concentrated. This is also our future failure or The place of focus when you are tired.
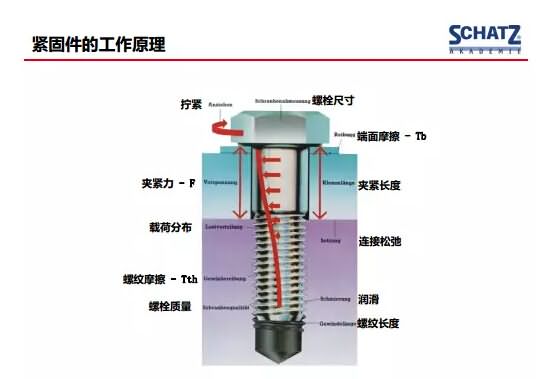
We introduced the clamping force of the bolt and then introduced the coefficient of friction. The relationship between the clamping force of the bolt and the torque. In fact, our coefficient of friction is a bridge. The bridge determines what kind of torque the clamping force is. The friction coefficient is simply derived from the ratio of our torque and axial force. relationship.
This is also very well understood. When you are in middle school, you can measure the physical friction coefficient and pull the square forward. You can measure the friction coefficient between the surface of the square and the table. The friction coefficient is related to the strength of the square and the quality of the square. The coefficient is our coefficient of friction.
Therefore, in the fasteners of the bolts, the coefficient of friction also follows the physical principle. The relationship between the axial force and the torque gives the coefficient of friction. If we control the torque on site and our fastener suppliers, or the friction coefficient of the connected parts, are stable, then we can control to get a very stable clamping force;

The above describes the working principle of the fastener, as well as the relationship between torque and axial force. Next, the definition of the lower friction coefficient and the test standard are introduced.
ISO16047, which is currently the internationally implemented test standard for the friction coefficient of bolt fasteners. This standard was also developed by our German company. It should be pointed out that this ISO standard is an international standard. At the same time, there are many enterprise standards on the market. The standards of the public, the standards of Ford, and the corresponding test standards of friction coefficient require careful study of different standards, because each enterprise Standards have more or less differences in the implementation process, and these differences may affect the friction coefficient determination or small differences in the calculation process.

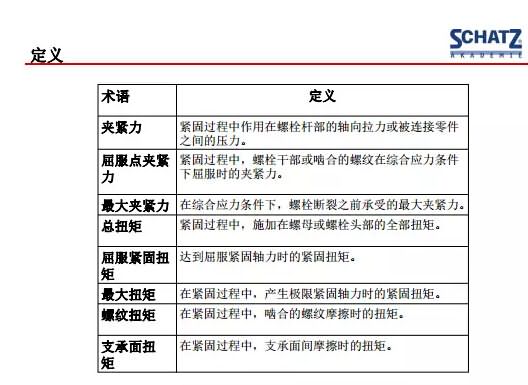
The content presented in this standard covers key data and results, definitions and calculation formulas; such as friction coefficient, total friction coefficient, friction coefficient of thread, friction coefficient of support surface, bolt yield torque and breaking torque How to calculate, this standard has a clear and detailed calculation formula.
The following picture can be passed through Schatz's friction coefficient test system. We call the Schatz Multi-Functional Fastening Analysis System. This software can be used to obtain the relevant test tightening curves according to different implementation standards, and automatically find the yield torque, axial force, and torque and The relationship of angles.
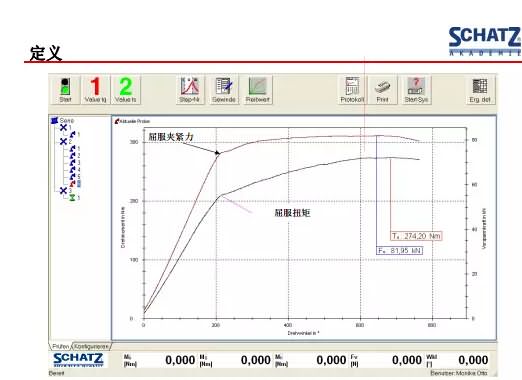
The friction coefficient and the tightening factor K, the maximum different friction coefficient is the friction coefficient divided into the head friction coefficient and the friction coefficient of the thread, which is beneficial to the design, process and quality management personnel, which can be clearly found in the manufacturing process. To improve or change the tightening state, it is corrected by the under head or the thread design. If the problem occurs, the thread or the coefficient of friction under the head is not well controlled.

With this design, the under head or the thread can be measured and processed separately. If it is a glued manufacturer, if it is to be glued on the thread and the coefficient of friction in the threaded part is clearly determined, it is possible to know precisely by the experiment whether the improvement on the thread changes the friction coefficient at that time.
The next two pictures are examples of software. It is clear on the software interface to find the tightening and torque angle curves and the applied axial force. At the same time, the total friction coefficient and the thread friction coefficient are observed through the chart. The friction coefficient of the support surface is The actual test situation.
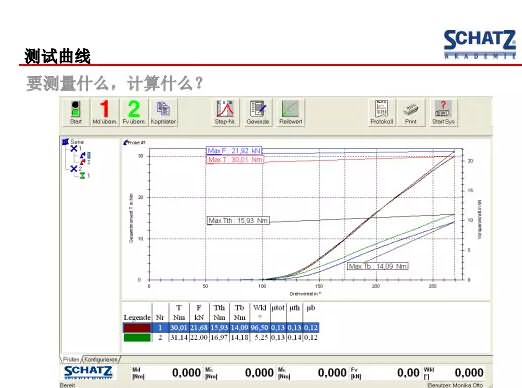
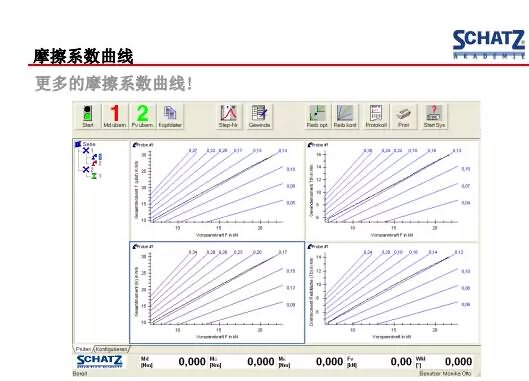
If we look through the ISO standard, the standard clearly confirms the state of the experiment, such as the speed of the tightening, the temperature of the experiment.
It is necessary to point out that there are many factors affecting the friction coefficient, and it has a relationship with the drilling speed, material strength, heat treatment and surface coating state. Therefore, in testing the friction coefficient, it is necessary to determine the experimental conditions, so that the experimental data of the friction coefficient is comparable. .

The next step is the axial force sensor. How is the friction coefficient measured?In fact, we set the tightening strategy, drilling speed, target torque according to the reliable tightening machine, and get the total torque and angle data. In addition, the picture shows the axial force sensor and the thread torque sensor, a composite sensor. The composite sensor can directly measure the axial force of the bolt during the tightening process, and also can measure the thread torque of the bolt during the tightening process in real time.

The figure below shows the discs and gaskets of our tooling. When we are making the coefficient of friction, the hardness and roughness of the gasket are detailed in the standard. According to the requirements, these gaskets can only be used once. After use, they must be re-polished.
In this way, the same contact state is maintained each time the friction coefficient is tested, so that accurate results can be obtained.

In the multi-function tightening and fastening analysis system, we can do two types of experiments, one is the standard friction coefficient experiment. Take the test bolt as an example. In the process of tightening, standard gasket and standard thread are needed. In the process, the test results can directly reflect some problems of the bolt itself; if it is the friction coefficient of the nut, it is necessary to use the standard bolt at the same time. Through the standard bolt, the test result can truly reflect the change of the friction coefficient of the nut itself.
Some customer feedback does not use nuts in the actual equipment, in the real state, what is the axial force. Then the second experiment is a process simulation assembly experiment. We need to use as much material as possible in the field assembly, including the nut, including similar clamping lengths. The closer the experimental state is to the actual assembly, the results of the laboratory test. The more the clamping force represents the real situation.
Related information recommended:
Determination of friction coefficient of fasteners (2)
Iron Wire,Iron Mesh,Wire Iron,Thick Iron Wire
HENGSHUI YUZHENG IMPORT AND EXPORT CO., LTD. , https://www.yzironnails.com