The derivation of the stress intensity factor K expression of a threaded fastener is how to solve the stress intensity factor of the root of the thread under the premise of considering the thread structure parameters. Some current methods use a similar typical crack body as the bolt model. After some corrections, the corrections are only for the structural parameters of the thread part, and the engineering is still not comprehensive. For example, if the thread is regarded as a grooved cylinder, the correction factor F of the stress intensity factor at the root of the thread is corrected only for the parameters such as the crack depth a and the cylinder diameter d; and the thread is approximately regarded as the thread according to the characteristics of the bolt. The crack, the correction factor F of the stress intensity factor at the root of the thread is corrected for the thread structure parameters such as the thread angle 0, the mutual interference between the threads and the radius of curvature d of the root of the thread. The effect is not yet fully unified by the derived smooth (non-grooved) cylinder stress intensity factor expression based on the expression of the shoulder stress intensity factor K derived by Liu Liu, due to the bolt and the cylinder with the shoulder The approximate shape of the body shape, and when the shoulder radius d shoulder is reduced to a certain extent, it becomes the thread fillet radius dm, thereby using the analogy derivation method, based on the analysis conclusion, considering the stress concentration, the thread tension The combined effect of the inter-angle interference between the angle 0 threads and the thread radius of the thread root d, see /d, d/D) is the correction factor; a is the bolt thread Among them: a/d item reflects the influence of crack propagation when bolt assembly connection is used, d/D item reflects Yin Feng et al. of bolt manufacturing: the influence of thread element on the fracture mechanical properties of the member.
It can be seen that the F'(a/d, d/D) data points tend to be linearly distributed. For convenience, the straight line equation is used instead: F(a/d, d/D) = 1.02-0.06, such as By substituting this linear equation into this, it is possible to find any crack length ai when the corresponding equation (4) (5) can be used to obtain the correction factor / (a ​​/ D) for each experimental data point (ai, Ni) can be found to correspond. /(a/d),. /(d/D) draw all the data points /, '(a / d) and /, U / D) on the coordinate paper, you can see their respective effects, see from it, not only the correction factor F(a/d,d/D) tends to be linear, and the correction factor /(a /D) tends to be linear, indicating that the F(a /D) hypothesis is true for further study of the correction factor / (a /D) and /(d/D) each provide convenience for the influence of the bolt stress intensity factor.
In order to test the effect of the derivation formula (1), it can be verified from another angle. The definition of da/dN=AaAN is defined by the higher mathematical differential, and the value of any point i can be obtained from the aN experimental graph, and Ni is corresponding to a. Substituting the value into the F(a /D) line d, d/D)Ae5, and finding (Ak), all the corresponding (AaAn), (AK)i data pairs obtained from the experimental curve aN are obtained from the theoretical value (da) i, (AK) i data pairs are drawn together under the same coordinates, the theoretical value is compared with the experimental value, if the range of use is the crack stability extension zone (0.53. 7mm), beyond this range, the crack tip plasticity The area is enlarged, beyond the linear elastic range, and the result of the Paris formula is invalid. 3 Conclusion From the experimental data, the cracking time of each bolt test piece varies greatly, which indicates that the manufacturing of the bolt raw material and the formation of the bolt test piece are formed. The effect of surface defects on crack propagation and fatigue strength is very large. It can be seen from the above that the correction factor f(d /D) of the inner and outer diameter of the bolt decreases with the crack propagation. When the crack expands to a certain depth, the effect disappears. This explains the theory Toribio's research conclusions are consistent. The stress intensity factor expression K of the bolt derived from this paper better describes the influence of the thread structure parameters on the fracture mechanics of the threaded fastener. The experimental results also show that the derived formula is closer to the actual Working conditions are reasonable and therefore have certain engineering use value.
Naipu ZJQ submersible Slurry pump is a kind of hydraulic mechanism which motor connects directly with pump.the pump adopts excellent material, advanced structure, and it is with wide flowing passage & strong delivery ability. The hydraulic parts are wear-resistant. The pump is yet completed with control unit. The pump set consists of main impeller and vice impeller. The main impeller is used for absorbing and delivering solid-liquid mixture, the vice impeller is used for spraying or stirring solid-liquid mixture to help the impeller delivering.
Typical Applications---
Delivering Liquid Sand, Coal Cinder Solid
Clearing The Mud In Lake, River, Sea
Dredging Widening Channel
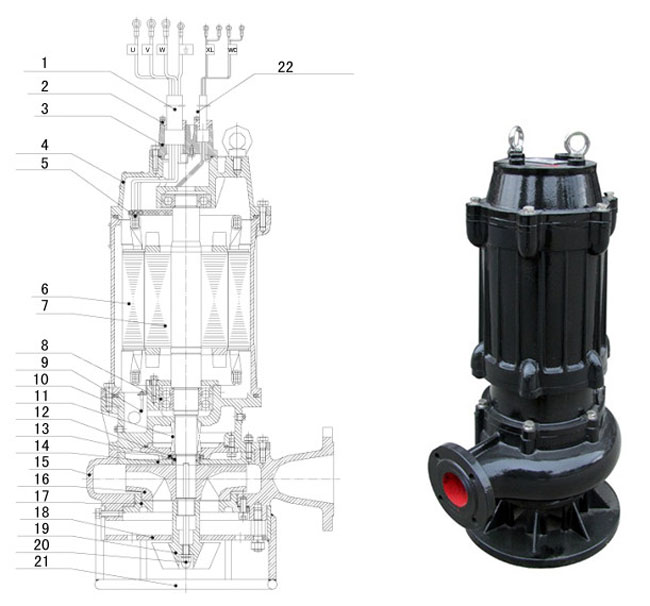

ZJQ Submersible Slurry Pump Configuration Drawing
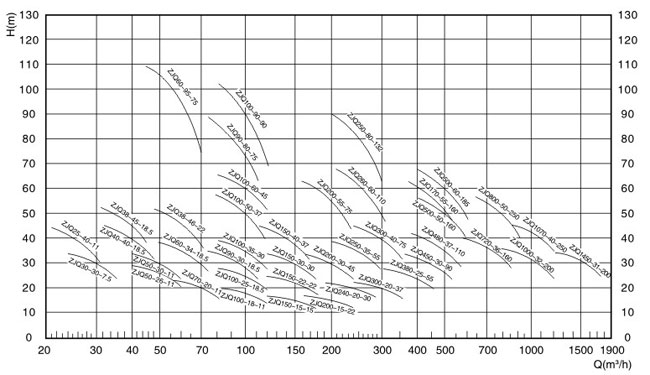
Performance Parameters

ZJQ Submersible Slurry Pump, High Chrome Submersible Pump, High Duty Mini Submersible Pump
Shijiazhuang Naipu Pump Co., Ltd. , https://www.naipu-pump.com