Dye-sensitized solar cell (DSSC) has the advantages of low cost, non-toxic and non-polluting, mild manufacturing process conditions, and suitable for large-area continuous production. It is currently a research hotspot of new solar cells. The semiconductor photoanode with a nanoporous structure is a core component of DSSC. The use of ordered, multifunctional new nanostructures to replace the traditional disordered photoanodes composed of nanoparticles is the forefront and difficulty of DSSC basic research.
The Shanghai State Key Laboratory of High-Performance Ceramics and Ultrafine Microstructure of Shanghai Silicate has recently made a series of new developments in DSSC nanostructured photoanodes. The research team led by Li Xiaoming researcher and Gao Xiangdong associate researcher developed a variety of ordered photoanodes based on TiO2 nanotube arrays and new composite photoanode materials based on aerogel structures.
Based on the long-term accumulation of research on oxide nanostructures, the long-term ZnO nanowire array was used as a template, combined with the continuous ion layer adsorption and reaction (SILAR) technology that can precisely regulate the nanostructure, and successfully realized the TiO2 nanotube arrays. Direct growth on FTO conductive substrates; unique hydrothermal roughening technology significantly increases the surface roughness, crystallinity, and dye loading of nanotube arrays. The photoelectric conversion efficiency of the resulting TiO2 nanotube array photoanode was 5.74%, which was 30% higher than that of the non-roughened nanotube array. On this basis, the research group obtained a coaxial, multi-walled TiO2 nanotube photoanode by successively depositing a multilayer of TiO2 and ZnO thin layers on the surface of a ZnO nanocolumn, and can precisely regulate the number of layers of the tube wall (1-6 layers). ) and thickness (5-15 nm); By growing dendritic ZnO and constructing ZnO-TiO2 core-shell structure, a TiO2 nanotube photoanode with a dendritic structure was prepared.
In aerogel composite photoanodes, the research group prepared SiO2-TiO2 composite aerogels using SiO2 aerogels with ultra-low density (0.03g/cm3) and ultrahigh specific surface area (1177m2/g) as templates. Then it was composited with the traditional photoanode of TiO2 nanoparticles to obtain an aerogel composite photoanode. Compared with the conventional nanoparticle photoanode, the photoanode can significantly increase the dye loading and the scattering effect on the incident light. The photoelectric conversion efficiency of the obtained DSSC reaches 9.4%, which is 16% higher than the conventional photoanode structure.
The above work provides a useful idea for the development of a new generation of dye-sensitized solar cells with controlled microstructure and high photoelectric conversion efficiency. The study was funded and supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (project number: 51072214, 51002174, 51102261). The relevant papers were published in Adv. Mater., 2011, 23, 1330-1334 (IF=13.877) and J. Mater. Chem. (2012.22.3549-35542012, 2012.22.18930-18938, 2012.22.23411-23417).
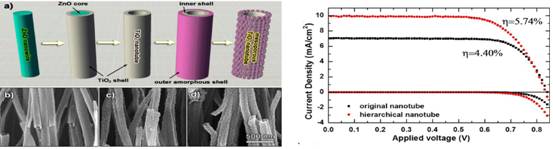
Preparation, Morphology and Battery Performance of Long TiO2 Nanotube Arrays
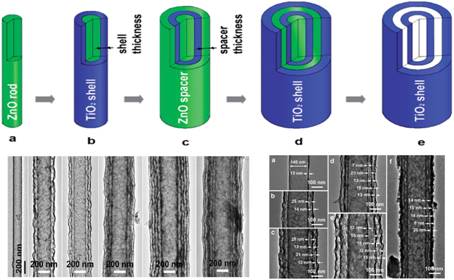
Coaxial and Multiwall TiO2 Nanotube Array Preparation and Microstructure
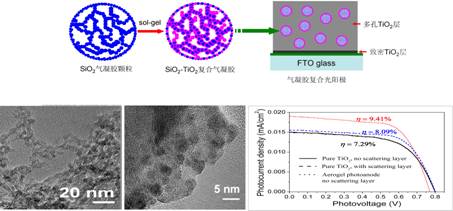
Preparation, Microstructure and Battery Performance of Aerogel Composite Photoanode
CHANGZHOU CLD AUTO ELECTRICAL CO.,LTD , https://www.cld-leds.com