Scientists in the United States have recently found an effective method to successfully convert lignocellulosic (ie, solid biomass) plants, such as switchgrass and poplar, into “green gasolineâ€. The research results helped to clear the key obstacles to the marketization of green gasoline. The leader of the study was George Huber, a chemical engineer at the University of Massachusetts, Amherst, who said that the future biofuels are chemically very similar to current diesel, and that chemical engineers face the challenge of adapting to the existing foundation. Under the conditions of the facility, find ways to efficiently produce liquid fuels from biomass. The new method uses a solid catalyst called “ZSM5†to quickly heat the cellulose and cause it to decompose. The role of the catalyst is to speed up the reaction process and reduce the unnecessary consumption of raw materials. The resulting product is then rapidly cooled to produce a liquid that contains a variety of gasoline components, such as fragrances. The researchers confirmed that the entire reaction process can be completed in two minutes, and the required heat energy is relatively moderate. Only this step can form 1/4 of gasoline components such as naphthalene and toluene. These liquids can be further processed to form other components of gasoline, or simply as a mixture of octane gasoline. John Regalbuto, director of the U.S. Science Foundation’s Catalysis and Biocatalysis Program, who supports the study, said: “Green gasoline can be used on existing engines and it will not incur economic losses. Therefore, compared to bioethanol, It is another attractive alternative energy source. In theory, green gasoline requires much less energy than bioethanol production, and the corresponding greenhouse gas emissions and production costs are also lower.†Regalbuto added: “The use of switchgrass and poplar trees as energy crops and cellulose sources also solves the full-cycle GHG issues of crop ethanol and soy diesel recently proposed by some scientists.â€
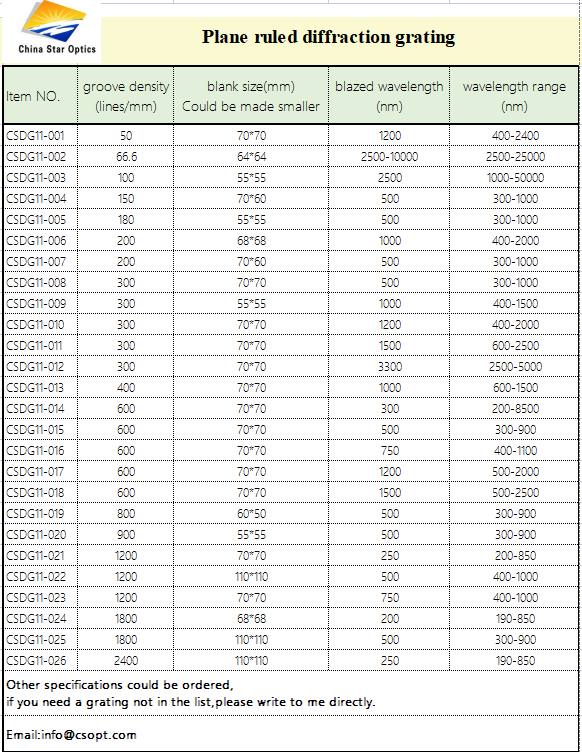
Plane ruled gratings are characterized by a superior efficiency at their design wavelength compared with holographic gratings. Plane Ruled gratings comprise the majority of diffraction gratings used in spectroscopic instrumentation and are especially useful in systems requiring high resolution.
China star optics can provide customers with a variety of replicated grating products such as diffraction gratings, reflective gratings,holographic gratings,concave gratings etc. to meet different needs. Maximum ruled area is up to 300 x 300 mm for plane ruled diffraction gratings. For replicated diffraction and transmission gratings the ruling density can be from 20 grooves per millimeter to 2400 grooves per millimeter, wavelength from 0.2 micron to 25 microns.
Holographic gratings:
Specifications:
Ruled area: <=70 * 70mm
Wavelength range: 0.2-0.8um
Grooves per mm: 1,200 to 3,600L/mm
Diffraction: >70%
Ruled gratings:
Specifications:
Ruled area: <=70 * 70mm
Wavelength range: 0.2-15um
Grooves per mm: 50 to 2,400L/mm
Diffraction: >70%
Concave gratings:
Specifications:
Ruled area: <=70 * 70mm
Wavelength range: 200 to 900um
Grooves per mm: 490 to 1,200L/mm
Diffraction: >70%
Plane Ruled Grating,Plane Ruled Diffraction Grating,Plane Reflection Grating,Plane Ruled Reflective Grating
China Star Optics Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.opticsrealpoo.com