Abstract: This paper introduces the production process parameters of sulphate electrogalvanized zinc with sulphur zinc-30 or sulphur zinc-40 as bright additive, the function of each component of the plating solution, the maintenance of the plating solution, the common fault treatment and the bright additive in use. Precautions. The parameters of bright galvanizing are given: 450-550 g/L of zinc sulfate, 20-30 g/L of boric acid, pH 3.0-5.0, bath temperature 10-60 ° C, brightener 16-20 mL/ L, the cathode current density is 10 to 45 A/dm2. Compared with the traditional sulphate single-salt galvanizing process, the bright electro-galvanizing process has the advantages of simple composition, stable and easy maintenance, fast deposition speed, low power consumption, fine coating and high corrosion resistance, and is suitable for producing high surface finish. Commodity wire.
Key words : electro-galvanizing; bright additive; sulphur-zinc-30; sulphur-zinc-40
CLC number: TQ153
The sulphate single salt galvanizing process is a traditional sulphate galvanizing process, which has the advantages of simple formula, mature technology, high current efficiency, fast deposition speed, good electrical conductivity and low price. Disadvantages are poor dispersing ability, low polarization ability, rough coating crystal, gray and dark appearance of the coating, poor surface finish, affecting the appearance of the product and the competitiveness of the product [1-4].
In order to overcome the shortcomings of poor surface smoothness of sulphate single salt galvanizing, various manufacturers constantly adjust the composition of the plating liquid additive, and some add sodium sulfate, aluminum sulfate, gum arabic or natural peach gum as a brightener, but the resulting coating is insufficient in gloss, and Resources are scarce. Use animal glue such as bone glue (gelatin) or dextrin, the coating is not bright, and the storage is easy to yellow. Adding nitrogen and sulfur compounds such as thiourea, there are defects such as poor plating, easy storage of ash, and reduced corrosion resistance [2]. In the 1980s and 1990s, a new generation of sulphate electroplating zinc brightening additive appeared in the country, which made the galvanized layer have a high degree of smoothness and good deep plating ability, and greatly advanced the sulphate single salt galvanizing process.
Since steel wire electroplating is not exactly the same as ordinary electroplating, it is a continuous electroplating of wire, short electroplating time and high thickness requirement. In production, strong circulation is often used to achieve high current [3]. Under continuous production conditions, the bath temperature tends to rise above 60 °C. Therefore, the brightener required to be added must be low in foam and wide in temperature range. In order to screen the sulphate galvanizing bright additive suitable for high-speed wire production, through repeated comparison tests on the sulphate galvanizing process of various types of bright additives in China, the sulphur-zinc-30, sulphur-zinc-40 bright galvanizing process technology was finally selected. . The process has the advantages of simple plating composition, strong anti-impurity ability, stable and easy maintenance, wide working temperature range, fast deposition speed, high production efficiency, low electric energy consumption, fine and bright coating crystal and strong corrosion resistance. The surface finish of the galvanized steel wire produced with bright additives is greatly improved.
1. Comparison of traditional electrogalvanizing process and bright electroplating process
1.1 Production process
Traditional electroplating zinc production process [3,5]: on line → electrolytic pickling → water washing → electrolytic alkali washing → hot water washing → weak pickling → electroplating zinc → water washing → passivation → high pressure water washing → hot water washing (with blocking agent) → baking Dry → take-up → inspection → sorting packaging → storage.
The bright galvanizing process is the same as the traditional electroplating zinc production process, except that the former adds a bright additive to the plating solution.
1.2 Process parameters
In the traditional electroplating process, the plating solution is used for circulating filtration. The galvanized steel wire produced by this process uses only the additional salt as a polarizing agent, and the cathode polarization is not large, so the plating layer is rough, the appearance of the coating is gray and dark, and the surface is gray. The smoothness of the finish is only suitable for the production of ropes that need to be processed continuously, and is not suitable for the production of commercial steel wires with high surface finish requirements.
The traditional electro-galvanizing process parameters are shown in Table 1.

The galvanized steel wire produced by the bright galvanizing process has a brightening additive (sulfur-zinc-30 or sulphur-zinc-40) as a polarizing agent, which greatly improves the cathode polarization ability, makes the coating grain fine, and has a good surface finish. The bright galvanizing process parameters are shown in Table 2.

2. The role of each component in the bright galvanizing solution
2.1 zinc sulfate
Zinc sulphate is the main salt of bright galvanizing solution. It mainly provides Zn2+ with a mass concentration of 450-550g/L. If the content is too low, it will affect the upper limit of current density and reduce the current density. If the content is too high, although the allowable current density can be increased, crystallization is caused by the solubility limitation, and the cathode polarization is lowered, and the formation speed of the crystal core is slowed, causing coarsening of the crystal grains of the plating layer.
2.2 boric acid
Boric acid is added as a buffering agent, mainly to keep the pH of the bright galvanizing solution controlled at 3.0 to 5.0. The degree of ionization of boric acid is small. When the pH of the anode rises due to the precipitation of hydrogen, ion ions can be ionized to maintain a certain acidity of the solution. Boric acid does not participate in the electrode process. It has no other consumption except for being taken out by the steel wire. Its buffering capacity has a function at 15g/L. If it exceeds 50g/L, it will be saturated and precipitated. Therefore, the mass concentration is generally controlled at 20~30g/L.
2.3 bright additive
The bright additive is prepared by mixing organic substances such as a carrier brightener, a main brightener and an auxiliary brightener. The carrier brightener mainly selects the substituent of active hydrogen and ethylene oxide on the hydroxyl group in the fatty alcohol, and the hydrophilic group is composed of both the ether bond and the hydroxyl group, and only one hydroxyl group at one end of the molecule is mainly composed of an ether bond. Play a hydrophilic effect. The main brightener is a high-quality aldehyde and ketone with C8 or C9 or higher with water-soluble or sulfonated groups. The aromatic sulfonic acid has good water solubility, such as o-toluenesulfonic acid and p-benzenesulfonate. The acid, m-benzenesulfonic acid and naphthalenesulfonic acid series have a certain gloss effect on the coating [6]. The auxiliary brightener can expand the range of bright current density, improve the crystal structure of the coating at high temperature, improve the performance of the coating, and improve the dispersion ability and deep plating ability of the plating solution. A good bright additive not only has good water solubility, good characteristic adsorption, but also good salt tolerance and good compatibilization. The salt tolerance of a brightener refers to the ability to maintain its carbon bond structure in a solution with a high concentration of the main salt. The higher the salt tolerance, the better the main salt concentration, the larger the current density allowable, the faster the deposition rate, the higher the line speed and the higher the yield. The poor salt tolerance of the brightener may cause defects such as yellowing, ashing, non-brightness, and increased consumption of the coating. The common plating bath has a dark brown oil, which is the brightener that can not withstand the concentration of the main salt. As a result, the brightener failure is caused [7]. The compatibilization of brighteners means that more aryl ketones can be combined to increase the active ingredient.
[NT:PAGE]As a bright additive, sulphur-zinc-30 or sulphur-zinc-40 can refine grains and improve the dispersion ability of the plating solution. It can produce characteristic adsorption on the surface of the cathode over a wide range of potentials, resulting in slow Zn2+ discharge steps and improved cathode poles. The formation is favorable for the formation of crystal nuclei, and the growth rate of each crystal face is evenly stretched, and the growth of the crystal grains is suppressed, so that fine crystal grains are obtained, and the plating layer is crystallized finely. The addition of the brightener can preferentially diffuse to the surface of the convex cathode for reduction, preventing the reduction of Zn2+, and the reduction and precipitation process of Zn2+ on the surface of the concave cathode is not affected, so that the unevenness on the surface of the cathode can be leveled. . The sulphur zinc-30 and sulphur zinc-40 additives are both a brightener and a leveling agent. When used as an additive, the coating can be finely crystallized and bright, which greatly improves the surface finish of the galvanized layer.
3. Maintenance and use of bright galvanizing solution
3.1 bath maintenance
The maintenance of bright galvanizing solution mainly pays attention to the following points.
(1) Keeping the plating solution clean is very important for electroplating an excellent zinc layer. Conditional units can be added with a circulating filter device to eliminate anode slag and other suspended solids in the solution to keep the solution clean.
(2) Each class of the plating solution is subjected to laboratory analysis and adjustment to keep the zinc sulfate, boric acid content and pH within the process range. When adjusting the plating solution, the prepared solution should be added to the outer tank (recirculating tank), and it is not allowed to directly join the inner tank.
(3) Addition of brightener. Brighteners are prepared by mixing organic substances. Due to their low content and complex composition, it is difficult to control by chemical analysis methods. When added, it can only be supplemented by experience, and the principle of keeping it plus less is always balanced. Less, the brightness of the coating is not enough; more, it is easy to make the coating yellow and black. In order to maintain a balanced addition, the simplest and most suitable method is to hang an inverted plastic bottle with a brightener above each plating tank, and insert a plastic infusion tube with a controllable flow rate at the mouth of the bottle. The metering brightener is added to the plating solution, thus avoiding the drawback that the initial content is gradually reduced after the brightener is added to the plating solution. When it is found that the brightener quickly fails after the addition of the brightener, generally the metal impurities or non-metallic impurities affect the role of the brightener, so do not continue to supplement, to avoid causing excessive brightener and affect the performance of the bath, should be removed before the impurities are produced.
(4) Pay attention to the relationship between temperature and current density. When the temperature is low, the conductivity of the plating solution is poor, and the strong desorption of the brightener is difficult. At this time, the high current density cannot be used. Otherwise, the blackening of the coating may be blackened or the embrittlement of the brightener may be increased, and the powder may be peeled off. The high-temperature brightener adsorbs weak polarization, and a higher current density must be adopted to increase the cathode polarization and refine the crystal grains. When the bath temperature exceeds 60 ° C, the bright additive decomposes faster and the decomposition product accumulates. When accumulated to a certain extent, a large amount of inclusions in the decomposition product adhere to the surface of the coating, which may cause brittleness, yellowing, fading, etc., which affect the quality of the coating.
(5) Foaming and heating of the brightener. During the electroplating, due to the movement of the steel wire and the circulation of the plating solution, a part of the foam is generated on the surface of the plating solution, and the temperature rises due to the coverage of the foam, thereby causing an increase in the consumption of the brightener. In the production, the foam should be removed at any time to prevent the foam from overflowing outside the tank and causing a "short circuit". Under the premise of ensuring the liquid level of the inner tank, reduce the number of circulating pumps, try to take the high level tank overflow to the lower tank, reduce the circulating agitation of the plating solution, and reduce the formation of the plating liquid foam.
(6) Harm and removal of impurities. When the content of metal impurities such as copper, lead and iron in the plating solution increases, the coating may be rough and the surface may be black, which seriously affects the surface quality of the coating. It can be removed regularly with 1-3g/L zinc powder. In order to reduce the cost, chemically pure sodium sulfide can be used for daily maintenance. The amount of 13mL/L can be effectively removed every time, but it can not exceed 15mL/L, otherwise it will be The plating solution has an adverse effect. A small current density electrolysis method can also be used to remove metal impurities such as copper and lead, but the treatment time is long and the loss of zinc is large. If treated with zinc powder, the electrolysis effect is better with a small current density. As the production time increases, the accumulation of decomposition products of bright additives increases. As the temperature of the plating solution increases, the decomposition of bright additives accelerates. After the accumulation of decomposition products increases, the appearance quality of the coating will be seriously affected. It must be treated with activated carbon to solve the problem. . During production, it should be treated regularly according to the situation. The method is to raise the temperature of the plating solution to 50 °C, add 3~5g/L activated carbon under stirring, continue to stir for more than 1h, and let it stand for filtration.
3.2 Operation Precautions
The following matters must be noted during the production of bright galvanizing.
(1) The surface of the steel wire before plating must be cleaned to prevent the zinc layer from falling off. In electrolytic acid and alkaline washing, it is necessary to control the current density and the concentration of acid and alkali, do not over-corrode, and the soaking time should not be too long. When the temporary shutdown occurs, the acid and alkali should be put into the outer tank in time. , the steel wire is exposed to the liquid surface in time.
(2) When the steel wire is operated in the electrolytic acid or alkali tank, the steel wire should be kept at a distance from the electrode plate. The parallel operation should not be twisted, and the plate should not be touched to avoid short circuit and shot, so that the surface of the steel wire is electrically damaged.
(3) The distance between the poles in the galvanizing bath, the relative position of the cathode and the anode also affects the uniformity of the coating. The steel wire in production should be 30~40mm away from the anode zinc plate, and run smoothly in the middle of the corresponding baffle. It should not be scraped with the separator or the base anode, and the liquid surface should not be exposed.
(4) The zinc anode plate is made by hot casting. The zinc plate must be installed in the zinc plate cover (anode sleeve). The anode sleeve should be regularly inspected and replaced to keep it intact. Check the consumption of zinc plate every shift. When the zinc plate consumes 2/3, it should be replaced immediately, so that the anode zinc plate, the electrode lead plate and the electrode bus bar contact are in good contact, and the anode zinc plate is in a normal dissolved state.
(5) During the operation of the steel wire, it should be pressed into the liquid surface by the negative gun 20~30mm. The flatness of the contact surface between the negative gun and the steel wire should reach the right angle of the top of the gun and the steel wire should be in parallel contact with the steel wire. Clean, every class should be checked to clean the head of the cathode gun to ensure good contact between the cathode gun and the steel wire.
(6) Remove the foam at any time during production, and reduce the number of circulating pumps while maintaining a certain height of the plating bath. The plating bath impurities are regularly treated and the plating tank is cleaned to ensure the cleanliness of the plating solution.
(7) The addition of brightener should be handled by a special person. In addition to zinc sulfate and boric acid, do not arbitrarily add conductive salts such as aluminum sulfate and alum, and brighteners in the plating solution, otherwise the production efficiency will be lowered and the plating solution maintenance will be troublesome.
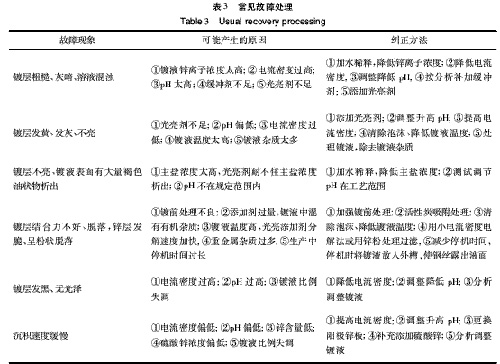
[NT:PAGE]3.3 Common Troubleshooting
See Table 3 for common faults, causes and corresponding treatment methods for bright galvanizing solutions.
4. Conclusion
Practice has shown that the bright galvanizing process is more suitable for the production of commercial galvanized steel wire, but there are some defects in the detectable, controllable, odor and low foam of the additive in the plating solution, and further improvement is needed.
References: slightly

Concerned about surprises
Tags: electro-galvanizing brightener plating galvanized steel wire additive
Previous: Fujian Province will check the heavy pollution remediation work of electroplating and chemical industry Next: Brush post-treatment: auto parts after brush plating
LED lighting system is widely used in airports, storage yards, squares, turntables, stadiums and other places.
Led Ceiling Light,High Power Spot Lamp,Dust Proof Led Light.LED Light
Henan Idui Import and Export Trade Co., Ltd , https://www.acesunraylight.com